Safety
Our Approach to Safety and Health
Tokyo Electron Group upholds the principle of "Safety First" as part of our Corporate Philosophy. In accordance with this principle, we give the highest priority to the occupational safety and health of all individuals, including management, employees, and the employees of business partners working within and outside the Group, as well as our suppliers and customers, in various business operations such as development, manufacturing, transportation, start up, and maintenance. We set goals to improve safety and good health and strive for ongoing, proactive improvements.
Our Safety Policy and healthy work environments are approved by the CEO and the corporate director in charge of safety and are applied to not only management and employees but everyone involved in our business.
November 27, 1998 Established
July 30, 2024 Revised
- Safety First
- Based on the principle of "Safety First," we strive to maintain and improve safety and provide healthy work environments for all employees, including the employees of partner companies working within and outside the Group, as well as suppliers, and customers.
- Legal Compliance
- We comply with laws and regulations, as well as international rules, guidelines and internal regulations pertaining to safety and health.
- Roles of Management, Supervisors, Employees, and Other Parties Engaged in Business Operation
- Management ensures operations are conducted with a "Safety-First" mindset, and the supervisors regularly audit safety and health management systems for continuous improvement opportunities. As a preventative measure to prevent work-related incidents, supervisors collect opinions from the site about safety in a timely and appropriate manner. Employees and other parties engaged in business operations are expected to always have safety at the forefront of their minds and are responsible for enhancing the work environment to ensure it is safe for all workers and visitors on site.
- Safety Activities
- We establish appropriate targets based on quantitative evaluation and analysis of safety activities and formulate implementation plans aligned with our priorities.
Employee representatives and relevant parties participate in Safety and Health Committee to discuss safety activities, share issues, and explore corrective and preventative measures. We work to deploy safety activities Group-wide and pursue ongoing improvements.
- We establish appropriate targets based on quantitative evaluation and analysis of safety activities and formulate implementation plans aligned with our priorities.
- Risk Assessments
- We identify risks involved in business activities, implement countermeasures, and evaluate their effectiveness.
We conduct quantitative analysis about hazard sources, scopes of impact, and frequency. We assess the probability and severity of incidents, including natural disasters and implement countermeasures based on priorities.
- We identify risks involved in business activities, implement countermeasures, and evaluate their effectiveness.
- Safety Training
- To raise employee awareness about safety and to build safer workplace environments, we develope training programs corresponding to the job responsibilities of employees and relevant personnel which are implemented Group-wide.
- Product Safety
- We adhere to international safety standards, country regulations and industry guidelines to provide customers with safe and reliable products.
- Equipment Safety Training
- We strive to prevent equipment-related incidents by providing appropriate equipment training for employees, other related parties, and customers to enable safe equipment operation. We actively disclose safety information and work to improve safety on a global basis.
- Communication
- We recognize that the basis of safety activities lies in fostering trust-based relationships. Management, employees, and related parties will strive for effective communication between all related people, including customers.
- Response to Disasters and Major Incidents
- In the event of extensive damage due to an earthquake, storm, other natural disaster, or an incidents, such as a fire, we will accurately ascertain the facts, prioritize protecting and rescuing human lives, and work together as one to quickly and calmly minimize losses, repair damage, and prevent recurrence. We have Business Continuity Plans in place in the event of a major incident and, will enact a Group-wide response under the direction of management, along with experts who will investigate the cause, and work to prevent recurrence.
Representative Director, President & CEO
Tokyo Electron Limited
We have established and operate a safety management system led by the CEO to provide a safe and secure working environment. Under the "Safety First" slogan, we have established the "Safety Policy" with the approval of the CEO and Corporate Officers Meeting, and inform all employees of the policy. We manage safety and health using an OHSMS*¹-based management system and implement the PDCA cycle to minimize the potential risk of work-related incidents and improve our safety and health management. We also progressively obtaining ISO 45001*² certification and carry out RBA*³ audits to ensure that our labor environments are safe.
Occupational Health and Safety Management System. A management system to improve the overall level of safety and occupational health.
ISO 45001 is an international occupational health and safety standard. In the Tokyo Electron Group, Tokyo Electron Korea, Tokyo Electron Taiwan and Tokyo Electron Europe have acquired ISO 45001 certification.
The Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) is an international initiative that promotes supply chain sustainability primarily in the electronics industry.
Safety Activities
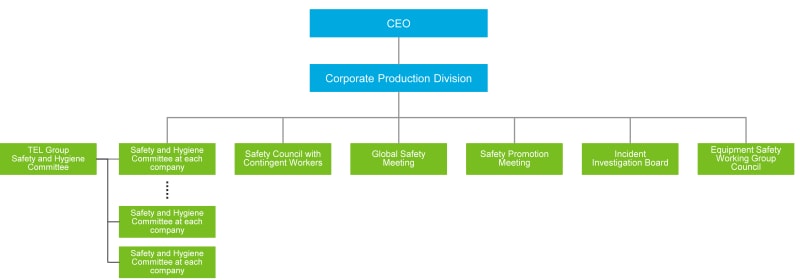
Global Safety Council
Personnel in charge of safety from each Group company gather once every six months at the Global Safety Council to discuss the state and results of safety activities, incident information, recurrence prevention measures and to share targets for the following term. Representatives from not only Japan, but from all Group companies including those from overseas participate in this meeting. Subcommittees for specialized fields are held where the issues and goals for each company are discussed among the personnel in charge.


Safety and Health Committee
Safety and Health Committee are convened monthly by employee representatives at each place of work. Participants discuss activities on workplace safety and employee health and safety and incorporate employees' opinion. Information from the Global Safety Council is also shared as a way of promoting Group-wide safety efforts. Information from the Global Safety Council is shared to promote Group-wide safety initiatives throughout the TEL Group. In addition, each place of work on incident prevention, with representatives of each department regularly conducting safety patrols at least once a month.
Premises Safety and Health Council Meetings
This meeting is held regularly every month to share information concerning safety at the workplace with suppliers. Suppliers and our personnel in charge of safety cooperate and hold numerous discussions on issues through which we advance Group-wide initiatives that suggest and implement revisions to maintain workplace safety.
Sakura Meeting
The Sakura Meeting, hosted by the Safety and Quality Promotion Office (SQP), aims to reduce incidents and promote safety activities. Personnel in charge of safety and field engineer representatives from across the whole Group gather and hold discussions on themes such as deliberations on safety measures. The 2025 meeting was also held when cherry blossoms were in full bloom.

Regular Safety Inspections
In addition to mandatory servicing and maintenance under law and inspections recommended by manufacturers, we conduct inspections such as thermal imaging using infrared thermography to check for abnormal heat generation in standby power generators, other electrical equipment, rotating machinery (such as pumps and fans), and power transmission equipment (equipment including belts). These are carried out Group-wide.
By revealing issues in work safety and training methods in addition to safety management methods for equipment, these regular inspections assist each Group company with their voluntary activities for maintaining and improving their safety environments.


Safety Patrols
Representatives of each plant and place of work regularly conduct safety patrols at least once a month to prevent incidents and resolve issues. In addition, we also implement TOP patrols in which management also participates to increase safety awareness and to expand communication with management through dialogue. Furthermore, measures such as irregular patrols in corridors and work areas are conducted based on the level of danger and frequency of use to reduce the risk of falling.
Safety Campaign
A majority of incidents that occur in the Company include ergonomics-related, falls and collisions. To increase safety awareness among employees concerning such incidents, we conduct awareness activities, such as by communicating through lock screens of employees’ computers and videos using digital signage, as well as safety campaigns. To prevent fall-related incidents, we encourage acting safely in plants and offices as well as parking lots when employees come into work in the winter months.

Image of digital signage
Job Safety
We identify and remove potential safety and health hazards continuously basis and provide education and training as necessary. In addition, while improving workplace environments based on suggestions by employees, we also implement improvements in the workplace environment through mitigation or removal of labor environment hazards and occupational safety and health risks for pregnant women, nursing mothers, young and elderly workers and all individuals with specificed disabilities.
Risk Assessment
We conduct risk assessments based on the "Risk Assessment Guidelines" and "Equipment Risk Assessment Execution Standards."
We provide feedbacks and use the results of the risk assessments to improve the work environment, revise work rules, and enhance the safe design of equipment. In addition to these improvements, we are also continually reviewing our work procedures and improving the way chemical substances are handled in various equipment.
Furthermore, under the leadership of the Safety Management Department, we are rolling out measures to prevent the recurrence of accidents resulting in personal injury, including at our each place of work and overseas subsidiaries.
Special Audits
In addition to regular internal audits, we implement special audits conducted by specialized groups to analyze incidents and to ascertain the realities of the scene in the event of major incident. We visit each Group company and the facilities in question to check on efforts relating to equipment in operating environments and activities to prevent reoccurrence.
Incident Reporting System
Accessible to all employees, the TEL Incident Report System (TIRS)* is used to quickly share information with the relevant personnel, confirm the current situation, and implement recurrence prevention measures. As a rule, incidents must be reported within 24 hours. Also, information on incidents and near-misses and hazards gathered through TIRS is stored in a database where the data is made visible from various angles and utilized for analyses on incident causes and trends using an application called the Safety Dash Board.
TIRS is Tokyo Electron Group’s TEL Incident Report System. The system is also used with all group company for report data aggregation, investigation of causes, analysis of trends and impacted personnel, and other activities as a recurrence prevention online system.
Near-Miss and Hazard Reporting
Reporting near-misses and hazards in addition to incidents is mandatory through TIRS and are shared in a timely manner with parties concerned. We send out training videos via email on examples of past incidents and post them on the intranet every other week for employees to access to prevent incidents. Near miss and hazard reports are offered in five languages, raising safety awareness in all employees.
As a result of these ongoing initiatives to reinforce safety worldwide, our LTIR*¹ in fiscal year 2025 was 0.32 and our TCIR*² reached 0.23, which is top class in the semiconductor production equipment industry. We will make further efforts toward achieving the target in our Medium-term Management Plan of a TCIR of 0.10 or less.

Heavy lifting training
| Data Concerning Safety | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | FY2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *¹ LTIR: Lost Time Incident Rate. Lost time incident rate per 1,000,000 work hours (LTIR) | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.83 | 0.31 | 0.32 |
| *² TCIR: Total Case Incident Rate. Number of workplace injuries per 200,000 work hours (TCIR) | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.15 | 0.23 |
Safety Training
Safety Foundation Training and Safety Technical Training
We offer "Safety Foundation Training" and "Safety Technical Training" globally as the two main programs for raising awareness about safety among employees and to create a safe workplace. As a compulsory training, "Safety Foundation Training" teaches the basics of safety to enable all employees to perform their operations safely in the workplace. We carry out introductory training for new hires and are working to improve employees’ retention of safety awareness by providing refresher training once every three years.
"Safety Technical Training" is a specialized program for engineers working on production lines or in cleanrooms. Contents are renewed annually, and refresher training is carried out each year.


| Percentage of employees who received training on safety | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | FY2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of employees who received training on basic safety | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Percentage of employees who received training on advanced safety | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
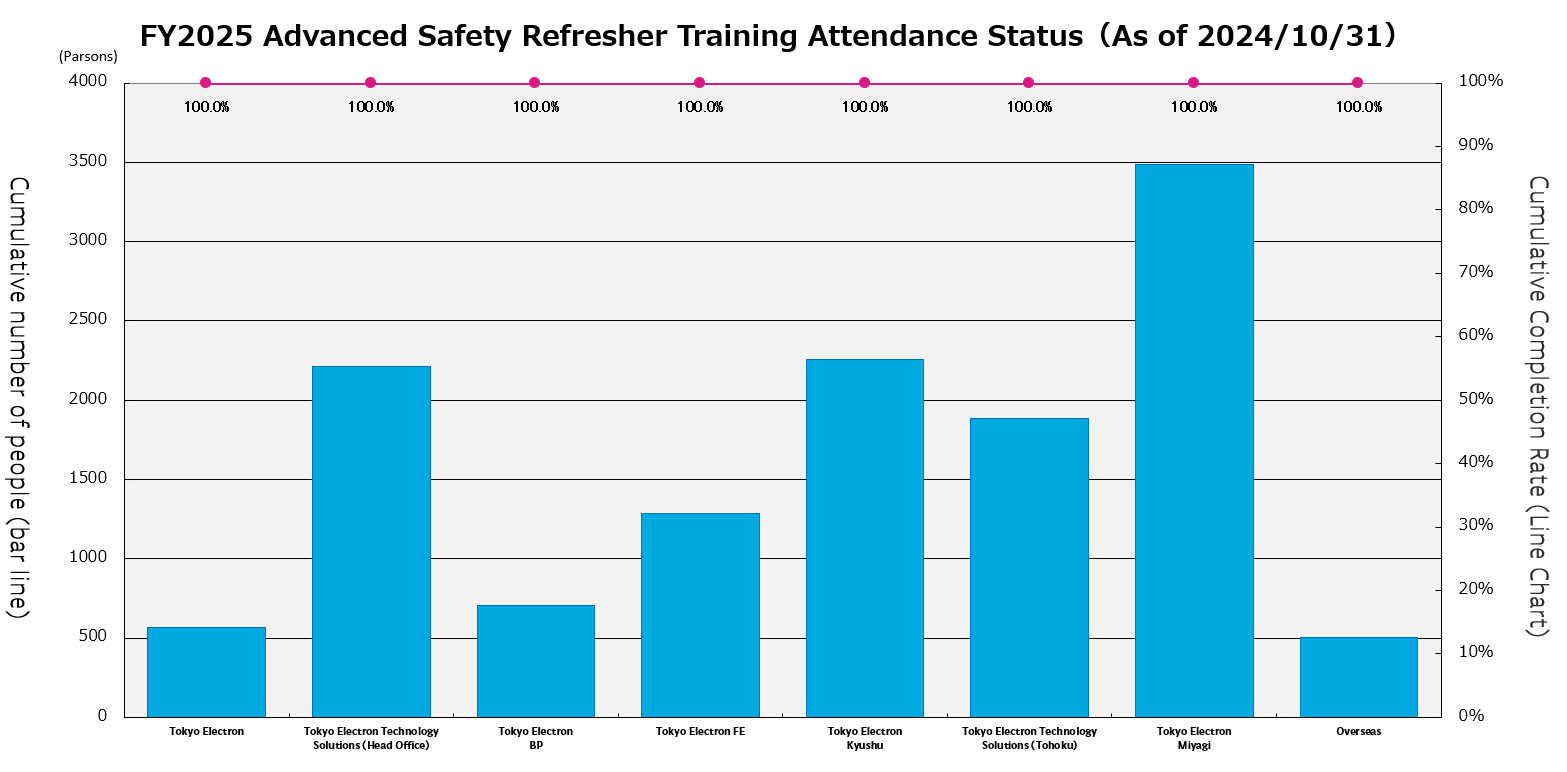
Percentage of employees who received refresher Safety Technical Training in fiscal 2025 (Numbers are rounded up to one decimal point)
Training for Overseas Transferees
For overseas transferees, we compare the laws and regulations in their previous and future places of employment and provide additional safety training as necessary. Additionally, training about safety rules and legislation in each country and region is provided.
Enhancement of Training Facilities
Tokyo Electron Korea established the TEK Safety Academy in fiscal year 2024 to raise employee safety awareness and enhance their incident prevention skills through practical hazard experience. The slogan followed is “Watch, Try, Feel and Experience Safety First.”
Furthermore, Tokyo Electron Shanghai also opened a new training center allowing practical training programs with a focus on experiential training (e.g. LOTO* simulation, heavy lifting).
LOTO: Lock Out Tag Out is a safety procedure used to prevent incidents and injuries that may be caused by the unexpected release of energy from facility or equipment.

TEK Safety Academy
A facility specialized for safety training that houses facilities for experiential training and a large conference room with a 60-person capacity. The academy also provides training in which the efficacy of protective equipment can be confirmed.
Use of VR and AI
In addition to experiential training such as traditional training in lifting heavy items, we also offer training using VR on incidents involving falls from heights and exposure to chemicals. A further new initiative involves plans to progressively begin specialized training for engineers who work on customers’ premises in addition to manufacturing and evaluation areas. To more accurately assess the level of understanding of the material learned, written exams are offered at the end of the training which are marked by AI.

Image of experiencing a falling incident
Product Safety
Safe Design of Equipment
We develop products based on the inherently safe equipment design*¹ approach. We conduct risk assessments from the product development stage and strive to reduce the risk posed to humans by reflecting those results in the design. Additionally, we conduct compliance checks through third-party assessment bodies to ensure conformity with international safety standards and SEMI Standards*².
Furthermore, we conduct global surveys on increasingly strict laws and regulations and strengthen our collaboration and frameworks with overseas subsidiaries so that we can respond appropriately to the safety regulations in each country and region to which we ship products.
Inherently safe design: A design concept that eliminates the cause of the machine’s harm to humans through the safety design of the machine
SEMI Standards: SEMI Standards are regulations formed by SEMI, an international industry body which serves manufacturers of semiconductor production equipment, display production equipment, PV power generation equipment, materials and the like, to unify all of these international industrial standards.
Provision of Safety-Related Information
We are committed to providing sufficient safety information on our products so that customers can safely use them. All our products come not only with a manual specific to the product specifications, but also a TEL Safety and Environmental Guidelines manual applicable to all our products. The TEL Safety and Environmental Guidelines manual is available in 12 languages* to ensure that customers around the world can understand the content accurately; it describes examples of potential risks associated with using our products together with the methods for averting those risks, as well as safety measures applied to products and recommended methods for product disposal, divided into such categories as chemical, electrical, mechanical and ergonomic.
If new safety warnings are identified after a product ships, we promptly report these to the affected customers.
We also ensure that necessary information is communicated to customers to whom we deliver products that involve the use of particularly hazardous chemicals or high-voltage electricity.
12 languages: Japanese, English, German, French, Italian, Dutch, Russian, Portuguese, Korean, Traditional Chinese, Simplified Chinese and Finnish
Feedback on Equipment Safety Specifications
If changes relating to safety specifications are requested by customers, or if an incident occurs as a result of equipment design, we provide the information to the Production Design Department as feedback and have established an organizational structure that will move forward with the necessary discussions as quickly as possible.
Equipment Safety Training
Equipment Safety Training
To entrench inherently safe equipment design* approaches in design through to manufacturing and servicing operations, we conduct safe equipment design training at our manufacturing sites in Japan. We also promote our initiatives to prevent incidents, by providing our suppliers and customers with safety information as circumstances demand.
In recent years, it has become increasingly important for us to ensure compliance with international safety standards and guidelines early in the equipment design and development processes. Since fiscal year 2008, we have been offering its engineers web-based training on safe equipment design. Through risk assessment exercises and examples of actual incidents, the participants acquire basic safety knowledge for equipment design.
Inherently safe design: A design concept that eliminates the cause of the machine’s harm to humans through the safety design of the machine
Response to Disasters and Major Incidents
In the event of an earthquake, storm, flood, other natural disaster, or an incident or major incidents, such as a fire, we will prioritize protecting and rescuing human lives, and work together as one to quickly and calmly minimize losses, restore damage, and prevent recurrence under the instructions of management, based on the Business Continuity Plans (BCP) decided on.
In addition, we are also working on improving the quality of our BCP by conducting regular revisions and updates on our BCP measures according to the operational environment and situation.
For information on risk management and business continuity plans, see Risk Management in the About TEL section.
Disaster Drills
To minimize damage and confusion in the event of a disaster, we conduct regular disaster drills at each site.
At the Fuchu Technology Center, we conducted two daytime and nighttime disaster drills in March 2025. In the daytime drill, 653 employees participated and received emergency 119 call training in the event of an earthquake and subsequent fire, an evacuation drill and fire extinguisher training to prepare for initial stage fire extinguishing responses. Ninety-six employees participated in nighttime drills and practiced evacuations drills and roll calls in the event of a fire and tested the out of hour functions of the Company’s self-defense fire brigades at each site.
By engaging in such company-wide activities, we work on improving the Group’s overall ability to respond to emergency situations.
