Environment
Our Approach to the Environment
Tokyo Electron aims to solve environmental issues through our leading-edge technology and services under the slogan of "Technology for Eco Life." We strive to contribute to the establishment of a sustainable society by reducing our impact on the consumption of resources, on biodiversity, and on climate change by taking actions that both directly and indirectly contribute to the protection and conservation of the environment.
September 25, 1998 Established
July 1, 2016 Revised
- Environmental Goals and Continuous Improvement
- We establish environmental goals and continual improvement of the environmental management system to enhance environmental performance throughout our product lifecycle.
- Compliance with Applicable Laws
- We continually enhance our knowledge of environmental issues to not only comply with applicable laws, but also set additional voluntary standards.
- Environmental Contribution with Product
- We develop environmentally complimentary products through our leading-edge technology. TEL cooperates with our customers and suppliers to strive for the prevention and improvement of environmental impacts to contribute to a sustainable society.
- Operational Environmental Impact Reduction and Preservation
- We quantitatively analyze and reduce the environmental impact of TEL global operations, with activity from all levels of employees and operations to prevent pollution and protect the environment.
- Collaboration and Cooperation with Stakeholders and Society
- We actively promote collaboration and cooperation with all our stakeholders to achieve mutual understanding and conformance to expectations.
Based on the above-mentioned policy, we strive to reduce the environmental impacts on the entire value chain of the product lifecycle (planning, development, designing, procurement, manufacturing, logistics, use by customers, maintenance services, and disposal of products). In addition, the lifecycle of our products covers the time they are at suppliers we procure from, contractors used for development, manufacturing, and logistics, and customers the products have an environmental impact at. We strive to conduct due diligence by grasping potential environmental risks when we engage in M&A or newly enter projects. The above-mentioned policy is being implemented based on decisions made by the CEO and corporate directors in charge acting as highest decision-makers, and decisions are reflected onto management. Furthermore, this environmental policy is communicated both internally and externally to inform stakeholders of our company's approach to environmental initiatives.
Environmental measures are growing even more crucial. We have established an Environment Promotion Department in our headquarters, headed by our General Manager in charge of the environment. This department oversees multiple boards to promote efforts to address medium- to long-term environmental issues throughout entire Group. Environment Promotion Department, headed by General Manager in charge of the environment, has been established at the head office to promote environmental activities throughout the Group.
The Environment Council, made up of members appointed by the executives of the Group companies, sets targets related to environmental issues, monitors progress and also works to achieve its goals.
Furthermore, to continuously promote our environmental activities, we began operation of an environmental management system based on ISO 14001 since fiscal year 1998, primarily at our manufacturing subsidiaries. In March 2017, we obtained ISO 14001 certification for the entire group, which had previously been obtained at each plant and office in Japan. In accordance with this certification, we have identified environmental impact assessments and useful environmental aspects and are executing a standardized group format for environmental management programs and internal audit checklists. Continuing from the last fiscal year, we implemented improvement activities to achieve a total of approximately 100 environmental goals established for different levels as part of a Group-wide environmental management. Any issues identified through these activities are reviewed by the Global Environment Council and reported to the Manufacturing Companies Presidents’ Council. We were once again free from environmental incidents, accidents, violations and legal proceedings in fiscal year 2025.
*PFAS: Per and Poly Fluoroalkyl Substances. This is the collective term for perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl compounds, a subset of organic fluorine compounds.
| Conference Name | Participants | Function | Meeting Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Council for the Regular Reporting of Environmental Activities | CEO, Corporate Officer, manufacturing companies president, General Manager in charge of the environment | Report on matters discussed at the Global Environment Council and the TEL Corporate Environment Council and review items for approval | Quarterly |
| Manufacturing Companies Presidents’ Council* | Manufacturing companies president, General Manager in charge of the environment, etc. | Monitor and supervise progress related to environmental issues | Quarterly |
| TEL Corporate Environment Council | The GMs in charge of the environment and vice presidents of department, etc. | The promotion of environmental activities across the entire Group, set Group-wide goals | Appropriately |
| Global Environment Council | Appointed members by the executives at headquarters and the Group companies | Set individual goals related to environmental issues, monitor progress, work to achieve our goals | Twice annually |
At the Manufacturing Companies Presidents’ Council, information is shared on business affairs and issues regarding environment, safety, quality, supply chain management, etc.
ISO 14001:2015 Certified Plants and Offices
| Company Name | Plant/Office name | Certification Number | Certification Date | Update Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tokyo Electron | Technology Vision & Environment Strategy Department (Fuchu Technology Center) | 1124-1998 -AE-KOB-RvA | May 1998 | Mar. 2023 |
| Tokyo Electron Technology Solutions | Fujii Office/Hosaka Office/Tohoku Office | |||
| Tokyo Electron Kyushu | Koshi/Ozu Office | |||
| Tokyo Electron Miyagi | Taiwa Office | |||
| Tokyo Electron(Kunshan) | — | 130755-2013-AE-RGC-RvA | Mar. 2013 | Mar. 2025 |
| TEL Manufacturing and Engineering of America | Chaska Office, North Chelmsford Office |
EMS586278 | Mar.2013 | Feb. 2025 |
| Tokyo Electron Korea | TEL Technology Center Korea, Balan Plant | ESC2795 | July 2014 | Aug. 2023 |
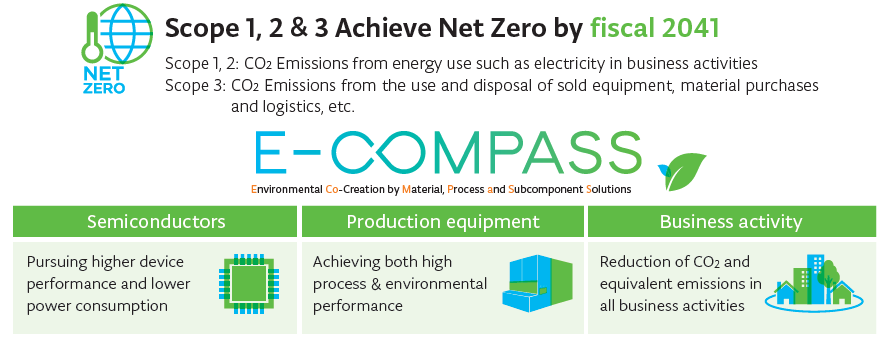
E-COMPASS
As a leading company in the semiconductor production equipment, we are rolling out the E-COMPASS (Environmental Co-Creation by Material, Process and Subcomponent Solutions) environment-focused initiative. Through E-COMPASS, we will work together with our customers and partner companies to promote semiconductor technological innovation and reduce the environmental impact of semiconductors through our business activities, centering on the three perspectives of semiconductors, production equipment, and business activities. We will supply products and services with technological and social value through our entire supply chain, led by E-COMPASS, and will link this to sustainable growth.
Initiatives with Suppliers
We believe we must accelerate our efforts even more to preserve the global environment and the data-driven society, which will be a growing reality in the years ahead. Four years have passed since we began our E-COMPASS activities and awareness about this initiative among many of our suppliers has increased. We are also making steady progress in each of our E-COMPASS projects and are achieving favorable results such as increasing the number of companies that have declared net zero. Leveraging these results, we will publicize our annual schedules and hold various events effectively to reinforce our collaborations with our suppliers even further.
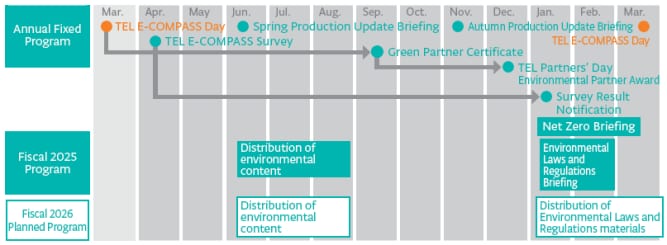
TEL E-COMPASS Day 2025
“TEL E-COMPASS Day 2025,” a briefing session with all our suppliers, was held in March 2025 using an online and in-person hybrid approach and was attended by 745 suppliers. At this briefing session, we shared information about the progress we have made in our E-COMPASS activities and our net zero efforts, and also provided detailed explanations on environmentally focused training materials, support plans and selection standards for environmental partners and green partners, and more. In addition, we engaged in lively exchanges of information with approximately 100 of our suppliers who attended the briefing session.
Measures to Reinforce Partnerships
To reinforce our partnerships, we are engaging in measures to understand environmental activities for each supplier and to offer partner certifications according to the details of those activities.
Sharing Information with Suppliers
We offer information we gather about the environment and share the activity details based on that information with all our suppliers. Achieving net zero by fiscal year 2041 will require cooperation in reducing emissions by our customers’ and suppliers’ production lines in addition to reductions in CO2 emissions within the Group. We have begun engaging in discussions with some of our suppliers and fleshing out measures to achieve these goals. We are also assigning persons in charge of net zero initiatives at each of our manufacturing sites and developing our internal systems. Going forward, we will work proactively to preserve the global environment across the entire supply chain through our partnerships with customers and suppliers.
Environmental Risks and Opportunities
Various environmental issues affect our daily lives and corporate activities. Physical risks, such as rising average global temperatures, strong winds, disasters and water shortages caused by climate change and abnormal weather, are expected to damage assets, increase operating costs and impact the supply chain. In addition, legal risks including stronger environmental laws and regulations, more stringent regulations on greenhouse gas emissions and the introduction of carbon taxes are expected to lead to higher costs for associated measures.
At the same time, promoting environmental initiatives leads to more opportunities to sell environmentally friendly products and reduce operating costs. We also recognize that providing high-value-added products that contribute to higher performance and lower power consumption of semiconductors leads to the building of an energy-saving society that makes the most of information technology, and thus provides an opportunity to improve corporate value.
Based on the requirements of ISO 14001, we identified and analyzed internal and external issues in relation to the environment, namely, our relationship with the climate, air quality and water quality. We also clarified the environmental needs and expectations of customers, suppliers, governments and employees and identified our compliance obligations as an organization. In addition, we define risks and opportunities to address as: (1) environmental management by reducing the environmental impact of our business activities, (2) compliance with applicable laws and (3) enhancing product competitiveness with the environmental contribution of products.
In addition, we are also considering risks and opportunities that are expected to occur due to the impact of climate change based on recommendations of the TCFD.
TCFD
Initiatives Related to Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
Based on the TCFD recommendations, we examine the risks and opportunities that climate change poses to our business and take various response measures as we endeavor to make disclosures high in transparency. In December 2023, we moved forward the target year for achieving net zero from 2050 to fiscal year 2041. In January 2025, we obtained SBT validation (1.5°C target) for our net zero emission targets. In addition, since fiscal year 2024 we have referred to the disclosure standards of IFRS S2.
IFRS S2: International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Sustainability Standards of Disclosure S2 Climate-related disclosures
Status of Initiatives Related to Recommendations of the TCFD
| Items | Contents | |
|---|---|---|
|
Governance
|
|
|
| Strategy |
|
|
| Risk Management |
|
|
| Metrics and Targets |
|
|
Refer to Risk Management
Refer to E-COMPASS, Initiatives with Suppliers (E-COMPASS)
Refer to Environmental Goals and State of Progress
Anticipated Risks and Opportunities of Climate Change Impact and Our Response
We conducted a climate change scenario analysis in accordance with the TCFD recommendations.
We refer to the 1.5°C scenario*¹for risks related to the transition to a low-carbon economy and the 4°C scenario*² for risks related to the physical impacts of climate change. We assessed the impact of anticipated risks and opportunities over the short-, medium-, and long-term, and clarified our response.
- Timeline: Short-term = five years or less; medium-term = 2030; long-term = 2050
-
Scenarios used: 1.5°C scenario (1.5°C temperature increase): IEA (International Energy Agency) Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario, RCP2.6 (low stabilization scenario)
4°C scenario (4°C temperature increase): IEA Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS), RCP8.5 (high reference scenario)
In addition to the above, we also refer to RCP4.5 (medium stabilization scenario) and RCP6.0 (high stabilization scenario) - Scope: The entire Group as well as the entire value chain including upstream and downstream
- Details deliberated: Existing and new regulations relating to existing and new businesses, technical risks, legal risks, litigation risks, market risks, reputational risks, and both acute and chronic physical risks
1.5˚C scenario: Scenario to limit the temperature increase from pre-industrial times to1.5°C
4˚C scenario: Scenario with no additional easing measures against climate change 93%
| Type (Scenario) | Risk or Opportunity Items | Timeline of Manifestation | Anticipated Risks or Opportunities | Impact on Tokyo Electron | Impact Evaluation*¹ | Our Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition Risks (1.5°C scenario) |
|
Short- to medium-term |
|
|
Low |
|
|
Short- to long-term |
|
|
Low~ High |
|
|
| Physical Risks (4°C scenario) |
|
Short- to medium-term |
|
|
High |
|
|
Medium- to long-term |
|
|
Low |
|
|
| Opportunities (Common) |
|
Short- to medium-term |
|
|
High |
|
|
Medium- to long-term |
|
|
Middle~ High |
||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
|
Impact evaluation: Sets out the findings of evaluations of the impact of risks or opportunities within Tokyo Electron.
Carbon tax: We referred to the International Energy Agency (IEA) Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario for the increase in tax associated with GHG emissions. 1 U.S. dollar was converted as 150 yen.
SEMI: A global industry association representing the electronics manufacturing and design supply chain
Suppliers’ BCP assessments: Surveys have been conducted since fiscal year 2014 for suppliers accounting for more than 80% of our procurement spend (more than 85% of our procurement spend from fiscal year 2023).
MAGIC: Positioning the diversifying semiconductor market as MAGIC (Metaverse, Autonomous Mobility, Green Energy, IoT & Information, Communications) and proposing solutions based on leading-edge technology and experience based on an extensive installation record
Advocacy: Social activities and awareness-raising efforts aimed at influencing decisions in politics, economics, and society
SEMI Semiconductor Climate Consortium: A consortium of semiconductor value chain companies established to accelerate greenhouse gas emission reductions from the semiconductor ecosystem
CO₂ Emissions Across the Value Chain
Based on our slogan “Technology for Eco Life,” we aim to resolve environmental problems through leading technology and reliable services, understand the environmental impact generated throughout our entire value chain and promote business activities to reduce that impact.
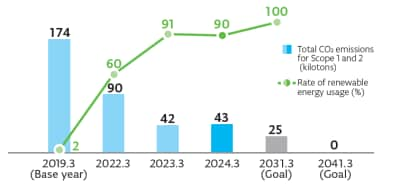
Our total CO₂ emissions of Scope 1 and Scope 2 is 47 kilotons, while Scope 3 as the sum of upstream and downstream activities accounts for a total of 12,694 kilotons, 99.6% of the total. Of this, CO₂ emissions when using products stand at 7,421 kilotons, about 60% of the total. This is why we consider the development of products with low CO₂ emissions during operation to be important.
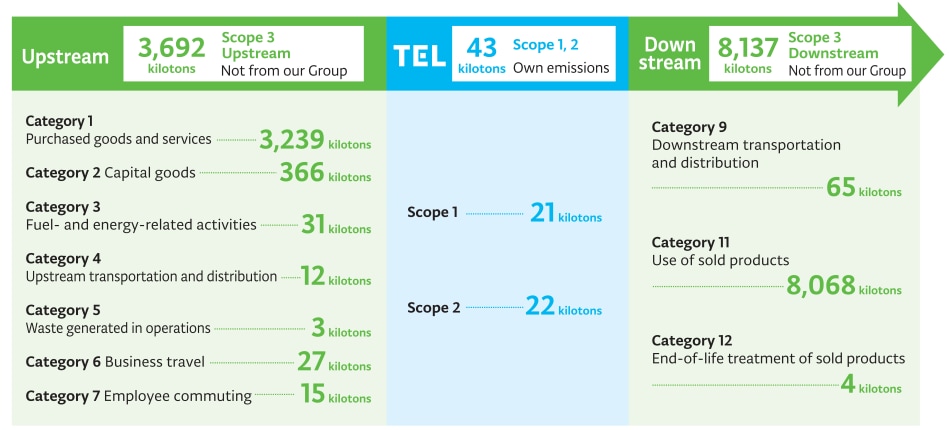
- Scope 1: Direct greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from use of fuel and gas we owned or controlled
- Scope 2: Indirect GHG emissions from use of electricity, steam and heat we purchased
- Scope 3*: Emissions from corporate value chains (excluding Scope 1 and 2 emissions), such as product transportation, employee business travel and major outsourced production processes
Scope 3 is divided into upstream activities, which include emissions associated with purchased or procured products and services, and downstream activities, which include emissions associated with sold products and services.
Environmental Goals and Progress
In December 2023, we moved up the target year of our net zero*¹ target for 2050 by a decade, to fiscal year 2041. We recognize dealing with climate change as a pressing global issue. We will implement various new measures, based on newly set targets. Through this, we will strive to protect the environment and actively lead efforts to achieve net zero emissions as a company of global excellence.
In October 2023, we received SBT*² certification from the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi)*³, recognizing that the greenhouse gas reduction targets we had set for fiscal year 2031 were scientifically based. Furthermore, net zero targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions across the whole value chain, including Scope 1*⁴, 2*⁵ and 3*⁶ set for fiscal year 2041, also received SBT certification in January 2025. As a result, we have received SBT certification both near-term and long-term targets.
Achievement of net zero greenhouse gas emissions from Group activities (Scopes 1 & 2) and from activities outside the Group (Scope 3) by fiscal year 2041
SBT: Science Based Targets. SBTs are targets that are set by companies for 5 to 15 years in the future and that match the standards required by the Paris Agreement.
SBTi: An international initiative that assesses and validates corporate GHG emission reduction targets.
Scope 1: Direct GHG emissions from using fuels and gases owned or controlled by the company.
Scope 2: Indirect GHG emissions from the use of purchased electricity, steam, and heat.
Scope 3: Emissions from corporate value chains (excluding scope 1 and 2 emissions), such as product transportation, employee business travel, and major outsourced production processes. Scope 3 is divided into upstream activities, which including emissions associated with purchased or sourced products and services, and downstream activities, which include those associated with sold products and services.
|
Targets recognized as SBTs
|
|
|---|
Initiatives Concerning Own Emissions (Scope 1 and 2)
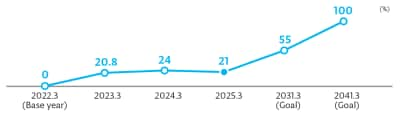
We aim to reduce total CO2 emissions from plants and offices by 85% (compared to fiscal year 2019 levels) and use renewable energy for 100% of our power by fiscal year 2031. By fiscal year 2041, we plan to achieve net zero. The ratio of renewable energy used in all companies in fiscal year 2025 was 89%. We have reduced total CO₂ emissions from our plants and offices by 73% also assisted by energy-saving activities. Going forward, we will continue to further strengthen our initiatives to reduce CO₂ emissions.
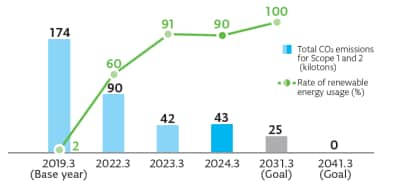
CO₂ emissions reductions from the introduction of renewable energy, etc.
Initiatives Concerning Emissions Not from Our Group (Scope 3)
We aim to reduce CO₂ emissions per wafer by 55% compared to fiscal year 2022 levels by fiscal year 2031. We also seek to achieve net zero emissions by fiscal year 2041. As of fiscal year 2025, we have reduced CO₂ emissions per wafer by 21% compared to the base year.
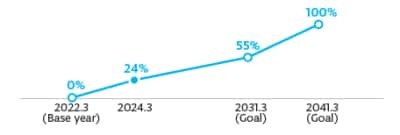
Reduction Rate in CO₂ emissions related to products
Achievement levels of goals
〇Proceeding well △Need to accelerate to achieve the goal
| Item | Scope | Target | Target FY | FY 2025 Results | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plants and offices |
Total CO₂ emissions | 85% reduction | 2031 | 73% reduction | 〇 |
| Renewable energy (electricity) | 100% | 2031 | 89% | 〇 | |
| Energy consumption (per-unit basis) | 1% year-on-year reduction | Maintain each year | Achieved by 6 out of 11 plants and offices | △ | |
| Water consumption (per-unit basis) | Maintain base year level | Maintain each year | Achieved 10 out of 13 targets | 〇 | |
| Products | CO2 emissions per wafer | 55% reduction | 2031 | 21% reduction | 〇 |
| Logistics | CO₂ emissions | 30% reduction | 2027 | 22.4% reduction | 〇 |
| Switch from wooden crates to STW* | 50% | 2025 | 34.7% over full year period (43.7% in fourth quarter) | 〇 |
STW: Strong Triple Wall. Reinforced cardboard made up of three layers.
Based on the roadmap for products to achieve the goals, for each product we calculated the reduction in consumption of electricity, process gases and chemicals, water, and other resources depending on how much of the above are consumed when the relevant product is manufactured or used, effects of the reduction in consumption of these resources, and the reduction in consumption due to improved productivity. In October 2023, we have received the certification from the SBT initiative* for our greenhouse gas emission reduction targets set for 2030 (Scope 1,2 and 3). Furthermore, net zero targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions across the whole value chain, including Scope 1, 2 and 3 set for fiscal year 2041, also received SBT certification in January 2025.We will continue to work as one company-wide on initiatives aimed at achieving net zero by fiscal year 2041.
Science Based Targets initiative(SBTi): The Paris Agreement aims to limit global warming to well below 2°C, preferably to 1.5°C, compared to pre-industrial levels. SBTi is an international initiative to certify greenhouse gas emission reduction targets set by companies for the next five to 15 years, consistent with the levels required by the Paris Agreement.
Progress in related initiative
- Reduction of water consumption: Initiatives to Conserve Water Resources and Reduce Water Consumption
- Reduction of waste: Initiatives to Reduce Waste
- Management of toxic substance emissions: Management of Chemical Substances, Initiatives for Product Environmental Laws and Regulations
Product Initiatives
Products that Contribute to a Sustainable Society
Of the CO₂ emissions from our value chain, emissions during product use account for about 60%. We believe that the low energy consumption of products is important as part of our social responsibility as a semiconductor production equipment manufacturer and are working on environmentally friendly product design.
One of our SBTs is to reduce Scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions from the use of the products we sell by 55% per wafer by fiscal year 2031 (in comparison to fiscal year 2022). Our actual reduction for fiscal year 2025 was 21% as a result of our efforts to promote the activities.
In addition, we use the Green Transformation (GX) Monitor, which captures information on energy use including electricity, water and nitrogen, as well as equipment operating status, and turns it into a database, to visualize energy consumption information during product use. Specifically, we have introduced a system that allows us to check equipment operating status and energy consumption information in chronological order through our intranet, and are planning to expand the scope of this system going forward.
We will continue to work to further raise environmental awareness and incorporate environmental technologies as important added value in our technological strategies, thus contributing to the reduction of the environmental impact of society as a whole.
Example Initiative1
In order to achieve the mid-term environmental goals for fiscal year 2031, we are developing and employing energy-saving accessories, improving the productivity of equipment through high-throughput*, and reducing consumption of utilities via flow rate control. Furthermore, we are also actively implementing activities such as enhancing the yields of product parts, increasing the lengths of maintenance cycles, stabilizing operations, and reducing footprints that indirectly contribute to reductions of CO₂ emissions and environmental loads.
Our new product, Ulucus™ LX, launched in December 2024, can reduce the amount of deionized water used by over 90% compared to conventional back grinding and edge trimming processes. Also, LEXIA™-EX achieves a 20% increase in throughput, a 40% reduction in footprint, and a 14% reduction in CO₂ emissions compared to conventional equipment.
throughput : the capacity of processing wafers during a certain length of time
Initiatives for Product Environmental Laws and Regulations
Our company proactively gathers information at an early stage to ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations related to our products in each country. We also promote proactive measures by providing our business partners with up-to-date regulatory information from various countries and promoting elimination and substitution of regulated substances in each market.
In addition, we have been introducing the chemSHERPA*³ format since fiscal year 2021 and collected information from suppliers on chemical substances in concentrations in the parts per billion (ppb*⁴). As a response toward GHS*⁵ requirements, we provide the necessary safety data sheets (SDS*⁶) and labels when supplying chemical products to customers, in addition to promoting the local procurement of chemical products.
To comply with the frequently revised environmental laws and regulations, we continue to offer “Product Environment Compliance” training to all employees, and provide suppliers with information related to the relevant environmental laws and regulations.
We will continue to grasp each country’s environmental laws and regulations rapidly and strive to respond appropriately.
chemSHERPA: A data entry support tool for appropriately communicating information on chemical substances in products across the entire supply chain, and a common system for communicating information on chemical substances contained in products
ppb: parts per billion (1×10-9)
GHS: Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals
SDS: Safety Data Sheet. Refers to the document containing hazard information about chemical substances that is issued when a company transfers or provides chemical substances, or products containing chemical substances, to another company
New York State 6 NYCRR* Part 494
We comply with New York State 6 NYCRR Part 494 - Hydrofluorocarbon Standards and Reporting.
For more information or to request a copy of the disclosure documents pursuant to NY Part 494, please contact: product.compliance@us.tel.com.
NYCRR: New York Codes, Rules and Regulations
Product Reuse and Recycling
Semiconductors are in greater demand and are becoming more diverse than ever. This has driven a corresponding rise in the need for more varied semiconductor production equipment. As a leading manufacturer of semiconductor equipment, we are strongly encouraging reuse and recycling of equipment and components by marketing refurbished our equipment and offering modification services to customers who already have our equipment installed.
Our refurbished equipment operations start with procuring used equipment from the market, which takes place either directly or through leasing companies. This equipment is then properly tested and refurbished, before being offered to customers as our Certified Used Equipment. Our equipment modification services boost the productivity of installed equipment by maintaining and improving its quality and availability. Through these approaches, we address our customers’ cost, speed, and performance needs, while also contributing to waste reduction and resource conservation and utilization. These efforts help reduce the use of resources and CO₂ emissions associated with procuring and manufacturing equipment and components. They are also effective in reducing the costs of production, logistics, and waste disposal.

Plant and Office Initiatives
Introducing Renewable Energy
We have set medium-term environmental goals of total CO₂ emissions at plants and offices by 70% (compared with fiscal year 2019) and rate of 100% renewable energy (electricity) usage at plants and offices by fiscal year 2031. For the fiscal year 2025, the ratio of renewable energy used in all companies reached 89%, achieving a 73% reduction in CO₂ emissions compared to the baseline year.
CO₂ emissions reductions from the introduction of renewable energy, etc.
All manufacturing sites, plants, and offices in Japan began introducing renewable energy in fiscal year 2023. Starting in fiscal year 2024, we expanded these initiatives to the U.S., and as a result, the transition to renewable energy has been completed at our sites in Japan, the U.S., and China. Going forward, we plan to further promote the adoption of renewable energy at our other overseas offices.
Example initiative
At Tokyo Electron Miyagi (Taiwa), monitors displaying the energy profile of renewable energy generated from solar panels have been set up at the entrance to the plant. At Tokyo Electron Kyushu (Koshi), renewable energy generation initiatives are being promoted, such as the sale of generated energy. In fiscal year 2024, a total of 3,901 MWh of renewable energy was generated in Japan. In addition, the Tainan Operation Center of Tokyo Electron Taiwan, completed in December 2024, uses electricity generated by solar panels. Through these efforts, we reached a total global renewable energy generation of 3,820 MWh in fiscal year 2025.
Initiatives to Prevent Global Warming and Save Energy
We have brought in a number of initiatives to achieve our medium-term environmental goal at plants and offices, including energy-saving cleanroom operation, setting office air-conditioning at appropriate temperatures, introducing devices that offer superior energy-saving performance and bringing in renewable energy.
Specifically, we are analyzing hourly and seasonal energy usage trends, usage efficiency and more, and we are identifying buildings, equipment and processes with especially high energy usage levels. We are also deliberating and implementing measures for cutting energy usage and for using energy more efficiently. Regarding the investments made in fiscal year 2025 to reduce CO₂ emissions, the cost is estimated to be approximately 24,000 yen per ton. It is assumed that the effects of these investments will continue for 10 years.
While we are still reaping the benefits of introducing renewable energy in Japan, the U.S. and China in fiscal year 2025, the amount of power being consumed in sites which do not use renewable energy is rising, and the CO₂*¹ emitted by our energy sources1 was 38 kilotons (a 19% increase year-on-year). Our power consumption was 472 GWh (an 8% increase year on year) due to the launch of operations in a new building and an increase in the amount of energy used by product development evaluation.
From fiscal year 2019, we revised*² and shared the per-unit basis for plants and offices in Japan to more appropriate levels based on the correlation between business operations and energy. In fiscal year 2025, we achieved our annual targets for per-unit energy sustainability at six of our 11 total plants and offices in Japan and overseas.
The emission coefficient for power consumption in Japan in fiscal year 2023 uses the post-adjustment emission coefficient on a per-electricity supplier basis, while the emission coefficients for power consumption overseas uses the emission coefficients in Emissions Factors 2019 edition issued by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
The per-unit basis is calculated by compound weighting using data on the number of development and evaluation machines, production volume, floor space, and man-hours in each region.
Energy Consumption and Energy Consumption per Net Sales
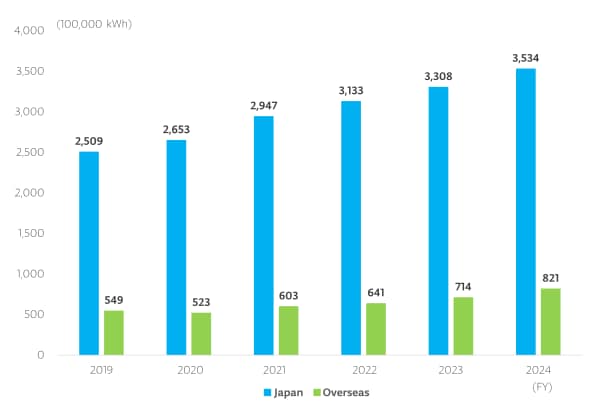
Example initiative 1
The introduction of a system to visualize clearly how much energy is saved at our plants and offices was completed at our major manufacturing sites in Japan in fiscal year 2022. Previously, energy consumption data had to be manually extracted and changes graphed by hand, but integrated management on the cloud has made it possible to check changes at any time. This has made it easier to check the deployment and effects of BKM* at each plant as well as study or implement measures.
More concretely, while in the past we were able to monitor increases and decreases in power consumption for entire business sites and buildings, now we are able to check increases and decreases for each piece of equipment such as refrigeration units, compressors, and lighting, making it easier to analyze and clarify the causes of increases and decreases in usage. In addition, this visualization system has made it possible to compare the effects of capital investment for energy conservation with pre-investment data for a more accurate understanding of the effects. We will accelerate our energy-conservation activities related to operations.
BKM: Best Known Method
Example initiative 2
Tokyo Electron BP holds Energy Conservation Competitions in which employees at each site are encouraged to offer ideas for achieving "net zero" (both Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions and water resource usage) that are feasible within three years. Excellent proposals are announced, reviewed and publicly recognized. In fiscal year 2025, the sixth competition was held and "Factory building heat source equipment integration" presented by Tokyo Electron Kyushu won the top prize. If this proposal is implemented, it is expected to reduce approximately 68 tons of CO₂ annually. These Energy Conservation Competitions provide us with new ideas about how to conserve energy and resources, and we will continue these activities in the future.
Initiatives to Conserve Water Resources and Reduce Water Consumption
With the growing importance of water resource preservation, we use WRI Aqueduct*¹ and freshwater resource quantity indicators to conduct water risk assessments in Japan and overseas*². In addition, we confirm the status of water resource use in the supply chain, rainwater and wastewater management and goal setting with suppliers once a year.
To achieve these goals , we analyze hourly and seasonal water usage trends, water usage efficiency and the like. We identify buildings, processes and equipment with particularly high water usage rates and consider and implement measures for reducing water usage and improving energy usage efficiency. Specifically, we are carrying out initiatives for cutting water usage such as reusing pure water from our manufacturing operations, installing water-saving devices for domestic water, watering lawns with rainwater, implementing the intermittent operation of cafeteria faucets and reusing runoff in combustion-based exhaust abatement systems.
We are also performing regular water quality studies to prevent any impact on our development or production processes. Water discharge is treated using water treatment facilities and then is confirmed to fall below legal and regulatory limits before being discharged.
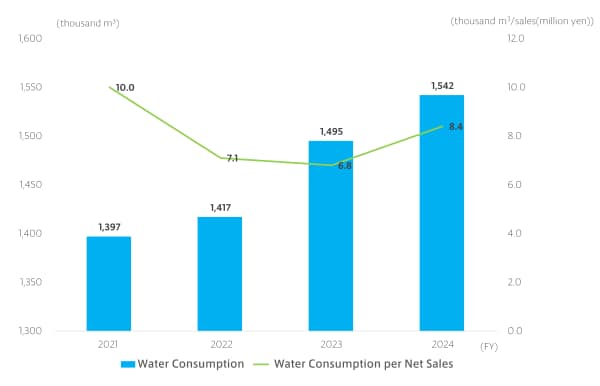
In fiscal year 2025, due to an increase in usage resulting from launching operations in a new buildings and performing product development evaluation, the amount of water consumption increased by 3% year on year to 1,587,000 m³. Water consumption per net sales also decreased 23% year on year, but we achieved our targets at 10 of our 13 plants and offices in Japan and overseas.
WRI Aqueduct: A water risk assessment tool developed by the World Resources Institute
Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures(TNFD)
Water Consumption and Water Consumption per Net Sales
Example initiative1
At Tokyo Electron Kyushu (Koshi), well water has been used. Due to pumping during water intake, sediments such as soil entered the water, so the pumped water was discharged until the water quality stabilized. To address this issue, filters were installed to improve water quality, allowing for stable water intake with consistent quality. As a result, the use of well water increased, and water consumption at the Koshi site in fiscal year 2025 was reduced by 7% compared to fiscal year 2024.
Example initiative 2
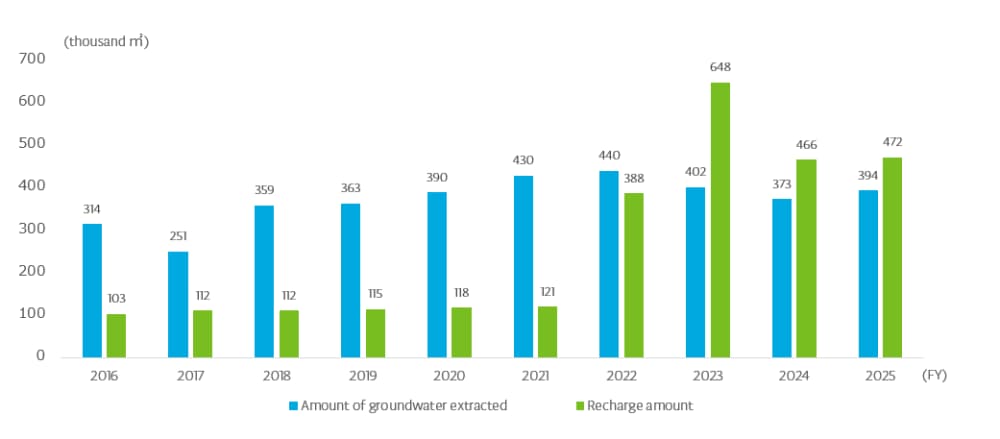
At Tokyo Electron Kyushu (Koshi), approximately 400,000 m³ of groundwater is currently used annually. Since fiscal year 2022, we have established a policy to replenish groundwater at least equal to the volume extracted (100% or more) in order to maintain a balance between groundwater extraction and recharge. Our groundwater recharge efforts have been progressing smoothly, and since fiscal year 2023, the amount replenished has exceeded the volume extracted. We will continue these groundwater conservation activities to protect valuable water resources in Kumamoto going forward.
The process of water soaking into the ground and storing as groundwater, including winter flooding of fallow rice fields and participation in rice farming activities.
Initiatives to Reduce Waste
To reduce waste, we are striving to curb the amount of waste we generate and to recycle waste. In addition to using an electronic manifest system*¹ to properly manage waste, we are confirming statistical data regarding waste and performing on-site equipment confirmation to assess waste production trends and their causes. We are identifying buildings, processes and equipment which generate particularly large amounts of waste and implementing measures to reduce the waste they generate. These measures include separating waste and adding new processes. Specifically, to raise recycling rates and cut the amount of waste, we are thoroughly separating waste, thoroughly preventing the wasting of resources, rationalizing parts inventories, using reusable boxes for deliveries, reusing cushioning material and contracting with waste operators capable of performing recycling. Through these efforts we are reducing the amount of waste that is sent to landfills or incinerated without recovering energy. We are also renovating our waste storage sites to increase their capacity while reducing the frequency of collection. Through this, we are striving to not only cut waste processing costs but also to reduce environmental impact.
Through this, we are striving to not only cut waste processing costs but also to reduce environmental impact. Through these efforts, in fiscal year 2025 we produced 222 tons of waste to be incinerated without recovering energy or buried in a landfill and achieved a recycling rate2 of 99.2%. This marked the 19th consecutive year, starting in fiscal year 2007, that we have met our target of a recycling rate of 97% or above. We also maintained a high recycling rate at our overseas sites of 94.8%.
Electronic manifest system: A system in which, instead of using printed manifests to manage industrial waste, the flow of industrial waste products is managed through a communications network that connects information processing centers, waste generating enterprises, waste collection enterprises and waste disposal enterprises
Recycling rate: (Recycled amount/Amount of waste generated) × 100
Example initiative
At Tokyo Electron Kyushu, pallets that are partly made from ocean-bound plastics (recycled plastics known as OBPs) are used to store products in stock. Environmental issues related to plastic waste have been drawing attention in recent years. In particular, marine plastic waste is posing serious problems. OBPs, which are plastic waste disposed of in land areas within 50 km from the sea may, if left uncollected, flow into the sea as marine plastic waste and contaminate the environment. We use pallets made from OBP to help combat the problem of ocean pollution.
Management of Chemical Substances
We constantly monitor and manage our use and release of any chemical substances used in product development and manufacturing subject to the Japanese PRTR* law. Whenever we introduce a new chemical substance or change the way an existing substance is used, we check for environmental, health and safety risks beforehand and conduct appropriate processing after use such as by contracting expert vendors and using in-house processing facilities. In response to the Fluorocarbons Recovery and Destruction Law, we conduct simple checks, regular inspections and so on based on law in an effort to monitor the amounts of fluorocarbons filled and recovered.
PRTR: Pollutant Release and Transfer Register. A framework for tracking, tabulating and disclosing quantitative data on chemical substances that may be hazardous to human health and the ecosystem, including the amounts used and discharged into the environment and the amounts transferred (as part of waste) from the plants and offices
Biodiversity and Forest Conservation (TNFD)
Our business activities are made possible by biodiversity. We recognize that our business activities have some impact on biodiversity, so we work to protect this biodiversity. We set a goal of conducting ecosystem tours or conservation activities at our plants and offices in Japan at least twice a year. In fiscal year 2025, we held a total of 19 such events, with a total of 378 participants.
In fiscal year 2023, we formulated commitments to biodiversity and forest conservation with the approval of the CEO.
These commitments applied to our entire value chain, and at the 3rd TEL E-COMPASS Day, an event held in March 2024 for all of our suppliers, we shared the contents of these commitments and the measures we were conducting in relation to them.

Biodiversity and Forest Conservation Commitments
The benefits of biodiversity are essential for the sustainable development of society. However, human society’s activities are having a major impact on biodiversity.
Through “TEL’s Shared Value,” we are working to resolve social issues through business activities that make use of our expertise. We aim to realize “Net Positive Impact (NPI)”* across our entire value chain through ongoing initiatives to preserve biodiversity. We believe that promoting activities in partnership with our stakeholders will help to boost our corporate value in an ongoing manner. As part of these efforts, we aim to achieve zero deforestation through working proactively to protect forests, which are home to ecosystems comprising numerous organisms and which constitute important CO₂ sinks.
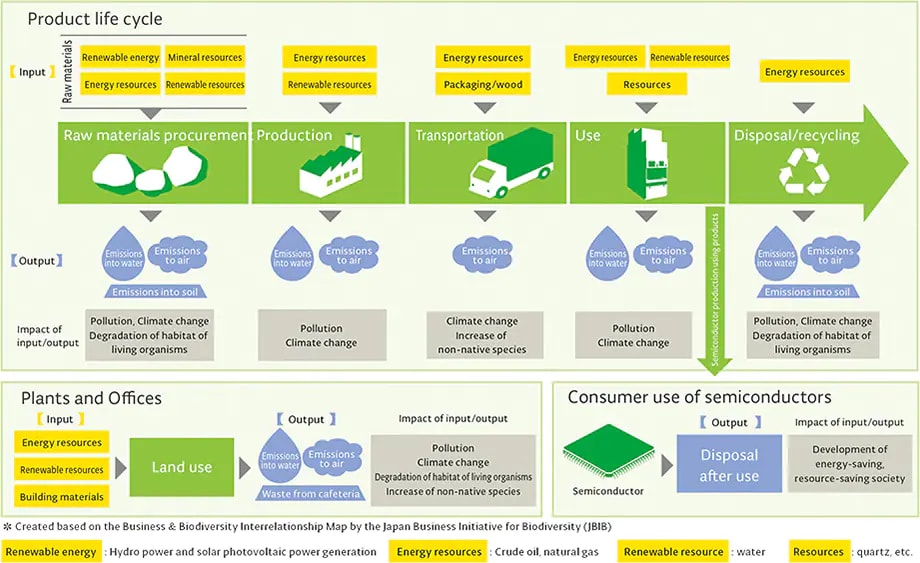
We make a map of biodiversity relationships based on the product life cycle assessments. We promote biodiversity initiatives based on the activity guidelines and the relationship map.
NPI: When loss of the natural environment cannot be avoided and the decision is instead taken to generate gains for the natural environment to offset the losses, ensuring that losses and gains are balanced constitutes “No Net Loss (NNL),” while going beyond this by ensuring that the gains outweigh the losses constitutes “Net Positive Impact (NPI).”
Interrelationship Map of Biodiversity Activities
Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures(TNFD)
Join the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures(TNFD) Forum
In July 2023, we announced that we concur with the vision of the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures(TNFD)*¹ and has joined the TNFD Forum, a group of institutions that support the activities of the taskforce.
TNFD is an international initiative established in June 2021 to support the transition to a nature-positive*² world, aiming to develop a risk management and disclosure framework for businesses with stakes in natural capital and biodiversity. The TNFD Forum was established in September 2021 as the taskforce’s support organization that provides expert insights and technical assistance to TNFD.
We are assessing the impact of our business activities on nature and the risks the loss of nature poses to our business. We are working to disclose this information in an appropriate manner. We will also collaborate with our stakeholders to enhance natural capital and biodiversity through our entire value chain.
The Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) was launched in June 2021 with founding members including the United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI), the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), and a British non-profit organization Global Canopy. With the aim of shifting global financial flows away from nature-negative outcomes and toward restoring biodiversity, the taskforce is developing a framework that drives businesses, institutions, and organizations to disclose risks and opportunities impacting natural capital and biodiversity.
Being “nature positive” means putting nature on the path to recovery by stopping and reversing the loss of biodiversity.
TNFD-based reporting
Having confirmed dependencies and impacts on biodiversity of our company’s businesses in fiscal year 2013, we prepared action guidelines to start our biodiversity initiatives. In fiscal year 2023, we formulated the commitments on biodiversity and forest conservation with the approval of the CEO. In fiscal year 2024, we joined the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) Forum to understand the basic overview of TNFD and the LEAP* approach that it recommends. Based on this understanding, we investigated the circumstances surrounding our supply chains and identified and compiled the latest information on priority locations . We also interviewed our suppliers to explore the current conditions and outlook concerning sustainability of raw materials. By obtaining information on measures against land use and pollution related to mineral mining, water consumed by manufacturing processes, and commodity production with risks , among others, we assessed the sustainability of raw materials as well as confirmed the current conditions for measures to be taken in the future to identify the traceability of the places of origin of raw materials and the environmental impacts of raw material procurement and to reduce these impacts. Furthermore, we assessed the following risks related to biodiversity.
Locate, Evaluate, Assess, and Prepare: Four steps of risk and opportunity assessment
Biodiversity risk assessment
Impacts and dependencies of our businesses on nature
We analyzed the impacts and dependencies of our supply chains on nature utilizing ENCORE (Exploring Natural Capital Opportunities, Risks and Exposure), provided by Global Canopy, a UK non-profit organization engaging in monitoring of corporate impacts and dependencies on nature, the UN Environment Programme Finance Initiative, and the UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC) . As a result, we identified that our upstream supply chains have large impacts and dependencies on nature.
|
Supply chain
Upstream
|
Our company |
Supply chain
Downstream
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependencies | Ground/surface water | High | Middle | Middle |
| Climate regulation | High | Low | Low | |
| Impacts | Water use | High | Low | High |
| GHG emissions | High | Low | Middle | |
| Pollutants (Air, water, and soil) | High | Middle | Middle | |
| Solid waste | High | Middle | Middle | |
| Noise/light pollution | High | Middle | Middle |
Risks
- Water risks
We analyzed risks related to water, such as flooding, droughts, and water stress, of each site in and out of Japan utilizing Aqueduct 4.0, provided by the not-for-profit World Resources Institute (WRI). As a result, it was found that our sites in China and the U.K. are located in areas with high water-related risks (Refer to Results of Analyses using Various Tools).
- Biodiversity risks
Concerning the potential impact of our business activities on biodiversity, we surveyed the numbers of IUCN Red List species*¹ and KBAs*² within an approximately 50 km radius from each site in and out of Japan utilizing Integrated Biodiversity Assessment Tool (IBAT), provided by UNEP-WCMC. As a result, we identified that large numbers of threatened species exist around our sites in Taiwan and Singapore.
Our risk analysis using the Biodiversity Risk Filter, provided by World Wildlife Fund (WWF), also revealed that our sites in China have high risks related to water quality, soil, and air quality (Refer to Results of Analyses using Various Tools).
IUCN Red Lis t: List of threatened wildlife species prepared by International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
Key Biodiversity Area KBA: Key areas for biodiversity conservation
- Deforestation risks
We surveyed the extent of deforestation over the past two decades in the areas where our sites in and out of Japan are located using the Global Forest Watch, provided by WRI, to grasp the forest conservation status. Korea has seen progress in deforestation, compared to other areas, with an approximately 18% decrease in the forest area over the past two decades (Refer to Results of Analyses using Various Tools).
Results of Analyses using Various Tools
| Aqueduct | IBAT | Biodiversity Risk Filter |
Global Forest Watch |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Stress | Water Risk | Water Pollution | IUCN Red list species* | KBAs | Scape Physical Risk | Deforestation Rate | |
| Japan | Middle | Middle | Middle | 1,444 | 7 | Middle | 4% |
| Korea | Middle | Middle | Middle | 926 | 7 | Middle | 18% |
| Taiwan | Middle | Middle | Middle | 3,220 | 5 | Middle | No Data available |
| China | High | High | High | 1,250 | 2 | High | 2% |
| U.S. | Middle | Low | Low | 968 | 2 | Middle | 3% |
| Europe (UK) | High | Middle | Low | 1,000 | 7 | Middle | 3% |
| Singapore | Low | Middle | Low | 3,192 | 7 | Middle | 13% |
Averages for areas with multiple sites.
TNFD Risk Analysis
| Type | Risk | Timeline of Risk Manifestation | Anticipated Risks | Impact on Tokyo Electron | Risk Evaluation | Our Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water |
|
Medium- to long-term |
|
|
Middle |
|
|
Medium- to long-term |
|
|
Low | ||
| Minerals |
|
Medium- to long-term |
|
|
Low |
|
|
Short- to long-term |
|
|
Low | ||
| Timber |
|
Medium- to long-term |
|
|
Low |
|
| Land use |
|
Medium- to long-term |
|
|
Low |
|
| Pollution (water quality, soil, solid waste, etc.) |
|
Short- to long-term |
|
|
Low |
|
| Opportunities |
|
Short- to long-term |
|
|
High |
|
|
Short- to long-term |
|
|
Low |
|
CMRT: Conflict Minerals Reporting Template. Survey format for reporting conflict materials, provided by the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI), which has established international guidelines on conflict minerals.
3TG: Tantalum, tin, tungsten and gold
As steps toward considering our measures against the water risks identified and specifying our commitments to biodiversity and forest conservation, we are planning to set indicators and action policies, perform detailed surveys of and activities in the surrounding areas of our sites, and engage in management of environmental and social risks related to minerals.
Example initiative
Tokyo Electron Miyagi has named a 4.2 ha area of prefectural forest in Yamato Town "Tokyo Electron Forest" as part of its efforts to nurture forests and preserve the environment, and has been conducting tree-planting activities (tree-planting events) since 2017. A total of 283 participants planted 324 trees in six years. In addition to planting trees and capturing trees, full-scale forest maintenance was carried out, including sorting out depleted trees and moving logs, and the participating children also had the opportunity to climb a cliff using ropes, make wreaths, and experience nature crafts.
In the sixth year of this activity, the forest, which was covered with dead and damaged trees before maintenance, is regaining its original appearance and has become like a park with a walking trail. In addition to the landscape, the number of shrimps, gentians, butterflies, and dragonflies in the ponds and puddles has increased, contributing to biodiversity.
Environmental Communication
Our environmental policy requires that we respond appropriately to the expectations of society. We promote initiatives for the environment while engaging in ongoing communication with all of our stakeholders.
In addition, to better promote environmental communication internally, we provide an environmental program for new employees and mid-career recruits, plus a refresher program for existing employees.
In fiscal year 2025, approximately 12,000 employees in Japan participated in the refresher program for existing employees. This training relates to our efforts to cut energy usage, our renewable energy initiatives, our efforts to reduce water usage and our initiatives for reducing waste and raising recycling rates, helping change employees' mentalities regarding these issues. In fiscal 2025, we will carry out an educational program for suppliers that will provide them with a greater understanding of our environmental policies and goals. Specifically, the training will cover topics such as Tokyo Electron's Environment Policy, our medium- and long-term environmental goals, the importance of environmental and climate change-related measures, abnormal weather and global warming and the methods used to calculate Scope 1, 2 and 3 CO₂ emissions from the supply chain .
Example initiative 1
At Esashi Plant in Iwate, employees participate in activities of "Oshu Megumi Net", a citizens' environmental conference in Oshu City. In fiscal year 2023, they are promoting communication through activities such as delivering a lecture titled "Environmental Activities: Technology for Eco Life" and participating in nature observation activities with local residents.

The Oshu Environmental Citizens' Council, known as "Oshu Megumi Net," was established to preserve the beautiful environment of Oshu City, and to pass on the spirit of environmental protection to future generations. Currently, approximately 100 individuals, companies, and organizations have joined and are actively engaged in its activities.
Example initiative 2
As part of our enlightenment activities aimed at providing increased opportunities to consider biodiversity, eco-life, and the environment through taking photos and/or painting pictures, we have been holding the TEL Eco-Life Art and Photo Contest annually since 2009. The contest, which is held for employees and their families, has attracted more entries every year. As many as 4,185 entries were submitted in fiscal year 2025 from the entire Group companies worldwide, with a grand total of over 15,000 submissions over the past 16 years.

Example 1 of the TEL Eco-Life Art and Photo Contest

Example 2 of the TEL Eco-Life Art and Photo Contest
Green Procurement
Green Procurement Guideline
We have been conducting business operations based on our environmental policy, which aims to conserve the environment and create a global recycling-oriented society. As part of this policy, we issued "Green Procurement Guidelines". We want every supplier to understand our sustainable global environmental conservation activities and these guidelines and provide us with your kind cooperation.
The Substance List (Revised Aug.20, 2025)
As global environmental laws and regulations become increasingly diverse and complex, we have prepared the TEL Substances List to reflect the latest laws and regulations and revise it. This documentation provides information on prohibited substances controlled during our business activities, the threshold values, and the reportable applications. If a substance designated as a TEL Prohibited Substance is contained, it must be decontaminated or replaced immediately.
Related Documents
As environmental laws and regulations regarding products are being strengthened, please refer to the following document for our approach and efforts to comply and conform to each law and regulation.
Request for Provision of Environmental Information Regarding Delivered Products
We are researching contained chemical substances used in all parts and products purchased from our suppliers.
Research on Contained Chemical Substance in Articles
We implement contained chemical substances in articles based on the TEL substance list.
We use chemSHERPA-AI* for the research on contained chemical substances in articles. The tool of chemSHERPA-AI can be downloaded from https://chemsherpa.net/english/
If you need more details about the research process, please contact us using the Sustainability inquiry form.
chemSHERPA-AI : The information transmission sheet to be used to communicate information about chemical substances contained in products
Research on Environmental Laws and Regulations
In addition to regulations on contained chemical substances, there are also regulations on energy efficiency and recycling in various countries. We are researching our suppliers and promoting their compliance with these regulations. We appreciate your cooperation.
Logistics Initiatives
Environmental Considerations in Logistics
Because of worldwide environmental concerns such as global climate change and the rising demand to reduce the environmental burden of logistics activities, transportation regulations are becoming more stringent. We continue to adjust our logistics operations to meet these demands.
CO₂ Reduction Initiatives
As logistics regulations are tightened from the perspective of preventing global warming and addressing climate change, there is a growing demand to reduce the environmental impact of business activities. We have been actively implementing measures such as a modal shift*¹ in transportation in Japan and overseas and the adoption of packaging methods that reduce environmental impact, as well as promoting activities designed to reduce the environmental impact of its logistics.
For logistics in Japan, we calculate and clarify CO₂ emissions within the scope defined by the Act on the Rational Use of Energy and Conversion into Non-Fossil Fuel, Etc. (Energy Saving Act). For logistics overseas, we calculate and clarify CO₂ emissions for both our Group companies and also for logistics in which our customers are serving as shippers.

Source: Tokyo Electron BP
In fiscal year 2025, we actively promoted the use of reinforced corrugated cardboard packaging and modal shifts to achieve our annual sustainability goal set in fiscal year 2021.
Strong Triple Wall (STW) is lightweight, which is expected to reduce CO₂ emissions from transportation. It is also recyclable and has a lower environmental impact than wood. For these reasons, we aimed to have a switchover rate of 50% or above from wooded crates to STW and resulted in 34.7% annually and 43.7% in the fourth quarter. Going forward, we will focus on standardizing STW packaging and promoting its use with customers. We will work towards an increased goal of a 60% or above switchover rate by fiscal year 2027.
In fiscal year 2025, we carried out activities to achieve our annual sustainability goal of further promoting modal shifts and joint delivery and reducing CO₂ emissions from overall logistics (own delivery) by 30% (by fiscal year 2027). As a result, CO₂ emissions from domestic logistics were reduced by approximately 5 kilotons (22.4%) compared with estimated emissions had modal shifts and joint delivery not been implemented.
These initiatives were positively evaluated, and we and Tokyo Electron BP, a Group company, were nominated for commendation by the Director-General, Maritime Bureau, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism in relation to the accreditation of the "Eco-ship Mark"*² for fiscal year 2023 organized by the Eco-ship modal shift business execution committee, as corporations that contribute to environmental measures through sea transportation, and were commended in May 2023.
Modal shift: Efforts to transform the means of transportation. Refers to the shift of transportation from car and air to rail and ship, which have lower environmental impacts.
Accreditation of the "Eco-ship Mark": The Eco-ship modal shift business execution committee organized by the Maritime Bureau of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, and operators of ferries, RORO ships, container vessels, automobile vessels, etc. awards the "Eco-ship Mark" to cargo owners and logistics operators that contributed to the modal shift to marine transport, and the Director-General at the Maritime Bureau of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism grants an award every year to an operator that made a notable contribution.
Example initiatives
We are proactively promoting modal shifts to reduce environmental loads. In fiscal year 2025, we replaced more than 5,000 trucks used for transportation between Osaka and Fukuoka with ferries.
Tokyo Electron Miyagi has been making modal shifts to railways to transport components from suppliers in the Kansai district. In fiscal year 2023, they started to carry out modal shifts for transportation of components from suppliers in the Hokuriku and Kyushu districts. Because modal shifts will contribute to the mitigation of "year 2024 problems" that are expected to reduce the number of available truck drivers as a result of strengthening of overtime work regulations, we will continue to proceed with this initiative. The usage of EV trucks was reinforced in fiscal year 2025, to 500 trucks used annually.
Resource-saving Initiatives
Because our products are precision equipment, they must be shipped with care and in clean conditions, requiring the use of wooden crates and cardboard boxes. To conserve some of these resources, We use recyclable cardboard boxes for packaging. After the equipment has been shipped and installed, casters and other specialized transport fixtures are collected and brought back to our factories for reuse. These are only a few examples of our resource-saving efforts.
