Research and Development
Research and Development for the Future
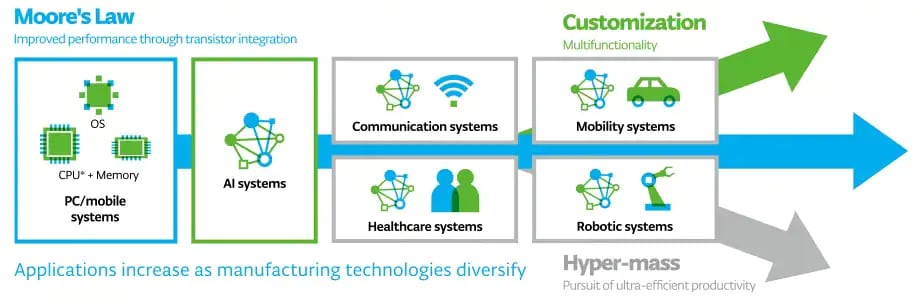
With the evolution of ICT, electronics are more and more indispensable to people’s lives. In addition, there is an increasing need to realize both the development of a data-driven society and preservation of the global environment, with the growing demand for semiconductors, which is the base of ICT and increasing global awareness of the environment. The performance required of semiconductors is also becoming more diversified.
In order to contribute to the development of a dream-inspiring society, Tokyo Electron is engaged in R&D with an eye on the future to capture changes in society, including innovations in manufacturing technology and the pursuit of ultra-efficient productivity.
Market Heading toward Diversification
CPU: Central Processing Unit. A semiconductor chip that serves as the brain of a computer.
Strengthening Research and Development Capabilities
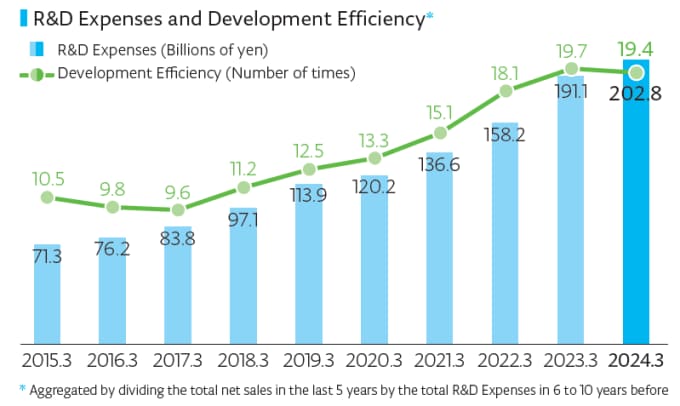
To continuously create the high-value-added next-generation products needed for technological innovation in semiconductors and bring them to the market in a timely manner, domestic and overseas development sites, our business divisions and the Corporate Innovation Division take advantage of their respective individuality and collaborate in necessary areas for us to promote technological development and integration. We construct development systems ranging from fundamental technologies to mass-produced products and promote DX that uses AI technologies in our R&D. In five years starting from fiscal year 2025, we will spend more than 1.5 trillion yen for R&D expenses to continue and accelerate these activities. In addition, by monitoring the contribution of the R&D expenses and their deliverables to net sales, we will check our development efficiency using R&D expenses in the past five years and net sales in the next five years to implement activities to further increase our development efficiency.
Each development site and business divisions have an eye toward future generations and are engaged in the development of innovative technologies. They also promote R&D related to peripheral technologies. The Corporate Innovation Division is developing cross-functional initiatives in each product area as well as promoting and optimizing R&D with a bird's eye view on the entire development structure. In addition, the division is also engaged in a search for potential growth areas, as well as in R&D of fundamental technologies toward creating value in the future.
For excellent deliverables of research and development in each site of our Group, awards from Global Awarding System as well as Excellence awards of our internal technology conference, Sustainable Technology Award and DX Award are granted to enhance engineers' motivation to create products.
Further Strengthening of Development Structure
We are actively investing with a focus on further growth as we endeavor to further strengthen our development structure.
To this end, we have completed construction of Miyagi Technology Innovation Center and a new development building at Tokyo Electron Technology Solutions Hosaka Office. We are also planning to open and operate new development buildings at Tokyo Electron Miyagi and Tokyo Electron Kyushu from 2025.

Miyagi Technology Innovation Center
(Completed in September 2021)

Tokyo Electron Technology Solutions
Hosaka Office New Development Building
(Completed in July 2023)

Tokyo Electron Miyagi
New Development Building
(Completion scheduled for spring 2025)

Tokyo Electron Kyushu
New Development Building
(Completion scheduled for summer 2025)
Shift Left
We are focused on using the Shift Left approach, investing resources such as technology, personnel and expense into the early processes of product development. Through this approach, we are endeavoring to develop various technologies and conducting research for multiple future generations to realize the technology roadmaps we have created with customers.
With product development through the Shift Left approach, we understand customer needs at an earlier stage, reflect the information obtained from feedback into our technological development and propose superior products. This contributes to maximizing yield for customer devices and capacity utilization of their mass production line equipment. We are also promoting on-site collaboration for early delivery of evaluation equipment to customers' fabs and development and research laboratories, and are working to accelerate the process in which technological development is reflected in mass production equipment as well as to optimize development efficiency.

Marketing
Based on the roadmaps of device technology and customer products as well as competitive analysis, marketing departments of business divisions, accounts and the corporate organization play respective roles appropriately and collaborate with each other to realize medium-term and long-term management plans.
Marketing departments of Business Units (BUs) in Business Divisions conduct planning of advanced next-generation products and promotion activities based on it to satisfy the needs of customers in the target market segments of respective BUs. On the other hand, marketing departments of account and corporate organizations conduct planning of integration that combines next-generation products of business divisions across BUs and planning of advanced new products not included in the product portfolio of business divisions to solve future High Value Problems (HVPs) of the customers. In addition, they propose solutions based on the above planning.
In the semiconductor industry, where business environment changes drastically, companies need the flexibility to change policies in a timely manner as circumstances require. Our marketing departments work together in performing their activities that anticipate market needs and contribute to customers' products as well as help improve our product competitiveness and promote our Shift Left approach.
Collaboration with Consortiums and Academia
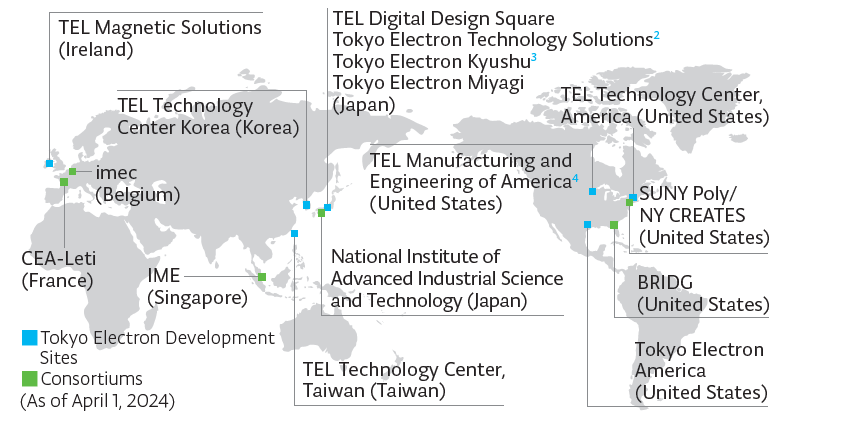
For many years, we have been focusing on joint research and development efforts with domestic and international consortiums and academia (universities). These initiatives help develop the development infrastructure to maximize the benefits of openinnovation-based development in each region. In recent years, we are also making efforts to boost human resource development in the semiconductor industry through collaboration with major universities in Japan and abroad.
We continue our development in various areas from applications to products through efforts such as R&D underway for the front-end and back-end areas at TEL Technology Center, America, participation in a global research hub for hardware development of next-generation AI, leading-edge logic development and quantum computing development, collaboration with "imec" in the logic process development and for patterning technology in EUV and high-NA EUV ranges, and collaboration with BRIDG, a not-for-profit, public-private partnership. In the semiconductor industry, in which the speed of technological innovation is rapid, developing new echnologies in advance is a source of corporate growth. We will not only develop leading-edge exposure technology but contribute to the creation of innovation with new structures/new materials such as CFET and TMDC*¹ by extracting and identifying technology change points by conducting market research with an eye towards ten years ahead.
In our collaboration with the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), one of Japan's largest public research institutions, we leverage its world-class research environment and personnel to enhance our own research and development capabilities by conducting development of leading-edge fundamental technologies required for diversified semiconductor device production and research in TMDC and 2D materials.
TMDC: Transition Metal Di-Chalcogenide, a material used for 2D transistors such as WS2, MoSe2.
Fujii Head Office, Hosaka Office, Tohoku Office
Koshi Head Office, Ozu Office
Chaska Head Office, Chelmsford Office
Intellectual property management
We are promoting intellectual property (IP) management under the fundamental tenet of contributing to an increase of corporate profits by supporting our business activities through IP protection and its utilization.
To achieve sustainable growth in the semiconductor industry where the growth is driven by technological innovation, we are globally expanding our R&D activity including industry-academia collaborations. Our IP department collaborates with R&D departments and business departments at each of our R&D and production sites, and with the marketing department at headquarters. The aim is to provide appropriate protection for innovations created based on development seeds and market needs, and to build an IP portfolio that is compatible with our R&D strategy and its shift-left focus.
In 2023, the number of inventions created in Japan was 1,186 and 303 overseas. We have maintained the global patent application rate approximately 75% for 5 consecutive years, and the allowance rate* of the filed patents has reached 81% in Japan and 80% in the United States. Furthermore, various inventions have been created through collaboration with domestic and overseas business partners, consortium and academia, and we have jointly filed patent applications on 61 inventions in the past three years.
Consequently, the number of active issued patents as of March 31, 2024 is 23,249, which is the largest number in the semiconductor production equipment industry, and we are building our competitive edge in the intellectual property field on a global level.
Our patent portfolio has also been rated highly for aspects such as impact on other companies and improved technological value over recent years. As in 2023, we have again been selected in the Clarivate Top 100 Global Innovators 2024 and the LexisNexis Innovation Momentum 2024: The Global Top 100.
We consider IP to be an important asset for improving medium- to long-term corporate value. We will therefore continue striving to improve the competitiveness of our products through differentiation of our technologies by building a competitive IP portfolio in terms of both quantity and quality.

Figures calculated in 2023
