- Semiconductor Technology Now
Report Series
Differences with traditional informatization
So how is digitalization different from automation and informatization? All of these trends use computers to process data. But in traditional forms of informatization and automation, computers were operating according to programs that contained work procedures and rules written by humans. For that reason, if the program had any mistakes (bugs) the computer would not operate as intended, and so it was important for humans to give instructions correctly.
The technology called digitalization differs significantly from automation or informatization in that the computer is not operating according to a program. Instead, it is a control system that uses information from sensors to make its own decisions. In the example of the rice cooker, the computer is being forced to operate according to the program, which is still within the realm of informatization. With digitalization or digital transformation, productivity increases are achieved without the need for human interaction by using computers and sensors to make the system change autonomously.
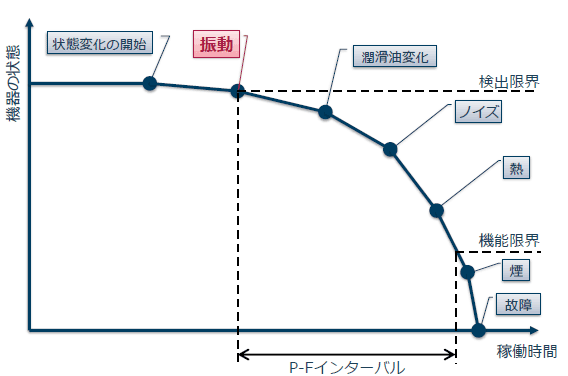
For example, a monitor for motors and pumps in a factory shows the conditions that a component goes through (Fig. 4). First, vibration levels increase, then the lubrication oil ages, next the noise becomes louder, and heats up. By using sensors to capture and predict these abnormalities, alarms can be fixed before leading to failures, thus preventing accidents before they occur.
In the past, experienced operators would regularly check the condition of motors and pumps for vibration, noise, and heat generation, etc. This required that they be able to pass this knowledge on to new recruits and newly assigned employees, but it was not always possible as they reached retirement age or changed jobs. If machines could generate alarms autonomously, factory downtime could be drastically reduced without relying on experienced staff.
 |
Sensors hold an important key
Sensors play an important role in digitalization. Sensors are devices that convert physical quantities such as temperature and humidity, motion (through detection of acceleration for linear motions and gyros for rotational motions), pressure, light, and so forth into electricity (voltage or current). If only one or two types of sensors are providing the data (electrical analog signal waveforms), individual circuitry is sufficient to make decisions without using a computer. However, if the number of sensors increases, and the data is complex in that it changes over time, then one or two circuits is not enough to make decisions. In this case, the computer must make a comprehensive decision.
The analog electrical signal waveforms from the sensor must be converted to digital for it to be easily handled by a computer. Of course, various processing must be done to the analog signal before it can be used, such as amplification and noise filtering. Once the sensor data is converted to digital and stored in memory, it can be retrieved as data at any time. Ease of storage is another feature of digital data, whereas storing analog waveforms in memory is extremely difficult.
If temperature and atmospheric pressure data is stored along with machine vibration data, and if the machine vibration changes significantly due to weather conditions, the cause of this vibration can be determined. The correlation between weather conditions and vibration can be judged based on a correlation factor, or the distribution of vibration can be calculated and used to formulate a relationship model between temperature and atmospheric pressure.
Computer-based comprehensive decisions can be made by a traditional computer, or artificial intelligence (AI). The computer could be programmed with judgment criteria that assumes a variety of conditions, or the computer could be taught a variety of assumed conditions to make it look as though the computer were making the decisions. This may also be called digitalization.
Analog technology is a must for digitalization
It is important to pay attention to the fact that digitalization makes use of numerous sensors and analog technologies. Japan is well-versed in sensors and analog technology, and has developed various sensors to date. For example, Professor Masayoshi Esashi of Tohoku University has been conducting R&D on MEMS (micro-electro mechanical systems)*3 sensors for more than 30 years.
 |
Footnotes
- *3
- MEMS: This is a technology that uses microfabrication techniques for semiconductors to make very small mechanical elements, such as a cantilever or drum-like structure, on silicon which is used to make sensors and actuators.



















